IoT SIMs for Remote Healthcare
Enhancing Patient and Clinician Experiences Globally, with a Focus on Asia
Transforming Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare
Introduction
Telemedicine and remote healthcare have emerged as vital components of modern medical practice, especially in the wake of global health challenges and increasing demand for accessible care. At the heart of this transformation lies the integration of multinetwork IoT SIMs—specialised SIM cards that enable devices to seamlessly connect to multiple cellular networks. Unlike traditional single-network SIMs, multinetwork IoT SIMs provide robust, uninterrupted connectivity, bridging gaps in geographical coverage and ensuring that critical health data flows reliably between patients and clinicians. Their relevance is growing rapidly as healthcare providers seek solutions that support scalable, secure, and flexible remote care.
How Multinetwork IoT SIMs Work
Multinetwork IoT SIMs are designed to operate across various mobile operator networks, automatically switching to the strongest available signal. This built-in redundancy mitigates coverage blackspots and minimises downtime. Technically, these SIMs utilise advanced network selection algorithms and agreements with multiple carriers, enabling devices—such as ECG monitors, blood pressure monitors, oximeters, and wearable health trackers—to maintain continuous connectivity regardless of location. The result is a reliable data transmission channel, essential for remote monitoring, teleconsultations, and the management of chronic conditions.
Connectivity advantages are particularly pronounced in rural or underserved areas, where single-network coverage may be patchy or non-existent. Multinetwork SIMs enable healthcare devices to remain online, facilitating real-time data exchange, secure messaging, and teleconferencing. This ensures that clinicians can monitor patients remotely, respond to alerts, and coordinate care without disruption.
Benefits for Patients
The adoption of multinetwork IoT SIMs in telemedicine brings significant benefits for patients. First and foremost, improved access to healthcare services is achieved as devices function reliably in remote, rural, or transient settings. Patients with mobility challenges, those living far from medical centres, or individuals in quarantine can receive timely interventions and consultations without the need for travel.
Continuity of care is another key advantage. Real-time data transmission from wearable and home-based devices allows clinicians to track patient progress, adjust treatment plans, and intervene promptly when anomalies are detected. This ongoing monitoring reduces hospital readmissions and supports proactive management of chronic illnesses such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Safety and personalisation are enhanced through secure, continuous data flows. Multinetwork SIMs ensure that vital health parameters are transmitted without interruption, enabling clinicians to deliver tailored care based on up-to-date information. Patients benefit from regular digital touch-points, fostering engagement and adherence to treatment regimens. The reassurance of knowing their health status is being monitored closely contributes to improved mental well-being and trust in remote care solutions.
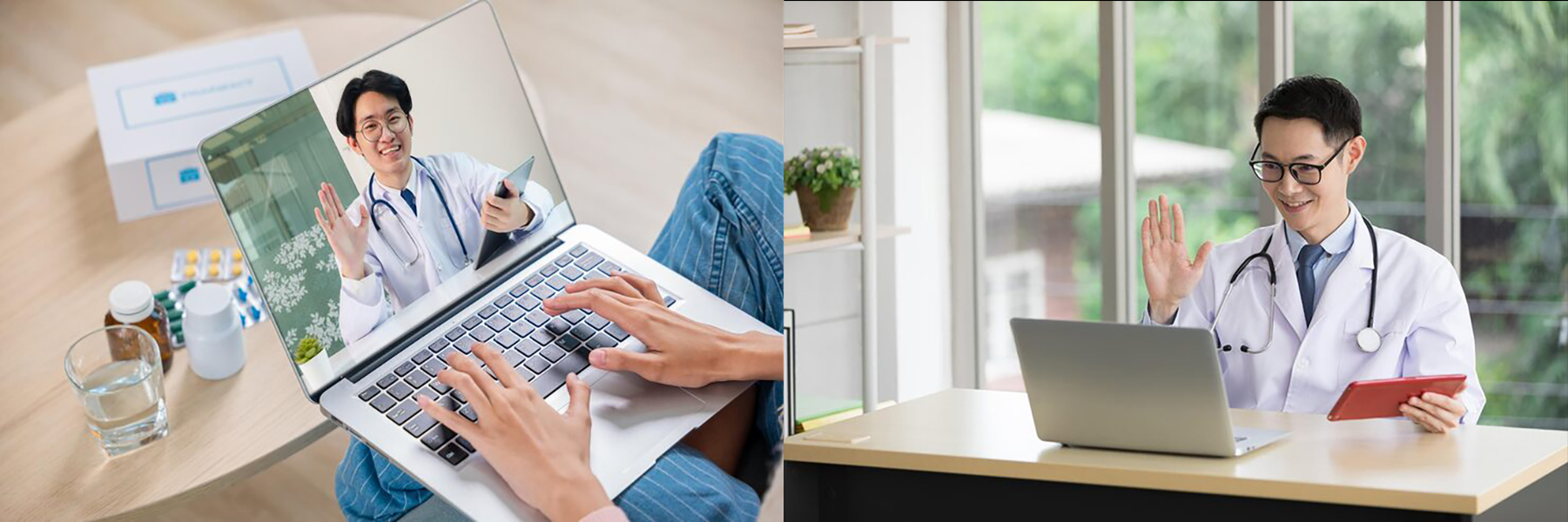

Benefits for Healthcare Workers
For healthcare professionals, multinetwork IoT SIMs offer a range of operational benefits. Enhanced collaboration becomes possible as devices and platforms remain reliably connected, supporting teleconferencing, secure messaging, and data sharing among multidisciplinary teams. This is especially crucial for complex case management, where input from various specialists may be required.
Access to real-time patient data streamlines workflows and supports informed decision-making. Clinicians can remotely review diagnostic data, respond to alerts, and adjust medications or therapies without delay. Such efficiency reduces administrative burdens and frees time for direct patient engagement.
Multinetwork SIMs also facilitate the rapid scaling of remote healthcare services. Devices can be deployed quickly to new patients or locations, with minimal technical overhead. This flexibility is invaluable during public health emergencies, when traditional healthcare infrastructure may be stretched or inaccessible.
Case Study: Impact in Asia
Asia presents a compelling case for the adoption of multinetwork IoT SIMs in telemedicine, given its vast and diverse geography, rapidly growing populations, and pronounced disparities in healthcare access. According to the Asia Pacific Telemedicine Market Report, telemedicine in the region is projected to grow at a compound annual rate of over 14% between 2022 and 2027, driven in part by advancements in connectivity solutions.
In countries such as India, Indonesia, and the Philippines, vast rural populations often face limited access to healthcare facilities. Multinetwork IoT SIMs have enabled the deployment of remote monitoring devices and telemedicine platforms, overcoming network fragmentation and expanding coverage. For example, a 2024 survey by the Asia eHealth Information Network found that over 60% of telemedicine deployments in Southeast Asia now rely on multinetwork SIM technology to ensure reliable service delivery.
Statistics further highlight the impact: In China, remote patient monitoring equipped with multinetwork IoT SIMs led to a 35% reduction in missed teleconsultations in rural areas during 2023. In India, government-supported telehealth programmes leveraging multinetwork connectivity reached an estimated 12 million new patients in hard-to-reach regions over the past two years. These figures underscore the transformative potential of robust connectivity in bridging healthcare gaps and improving outcomes across the continent.
Challenges and Considerations
 Despite the clear benefits, several challenges must be addressed to maximise the potential of multinetwork IoT SIMs in healthcare. Data privacy and security are paramount, as sensitive health information is transmitted across multiple networks. Robust encryption protocols and strict compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are essential to safeguard patient data.
Integration with existing healthcare systems can present technical hurdles, especially where legacy infrastructure is prevalent. Ensuring interoperability between devices, platforms, and electronic health records requires standardisation and collaboration among technology providers.
Additionally, digital literacy remains a barrier in some communities, necessitating targeted education and support for both patients and healthcare workers.
Connectivity challenges may persist in extremely remote or disaster-affected areas, even with multinetwork solutions. Ongoing investment in network infrastructure and policy support is needed to expand coverage and reliability further.
Despite the clear benefits, several challenges must be addressed to maximise the potential of multinetwork IoT SIMs in healthcare. Data privacy and security are paramount, as sensitive health information is transmitted across multiple networks. Robust encryption protocols and strict compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are essential to safeguard patient data.
Integration with existing healthcare systems can present technical hurdles, especially where legacy infrastructure is prevalent. Ensuring interoperability between devices, platforms, and electronic health records requires standardisation and collaboration among technology providers.
Additionally, digital literacy remains a barrier in some communities, necessitating targeted education and support for both patients and healthcare workers.
Connectivity challenges may persist in extremely remote or disaster-affected areas, even with multinetwork solutions. Ongoing investment in network infrastructure and policy support is needed to expand coverage and reliability further. Future Outlook
The evolving role of multinetwork IoT SIMs in global healthcare is set to accelerate as technology advances and adoption rates climb. Emerging trends include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for predictive analytics, enabling even more personalised and proactive care. Partnerships between governments, telecom operators, and healthcare organisations will be crucial in scaling solutions and addressing regulatory, technical, and educational challenges.
As 5G networks become more widespread, the capacity for high-bandwidth, low-latency data transmission will further enhance telemedicine capabilities. Multinetwork SIMs will continue to underpin resilient, efficient healthcare delivery, particularly in regions with complex connectivity landscapes.
Conclusion
 Multinetwork IoT SIMs represent a paradigm shift in telemedicine and remote healthcare, offering unparalleled connectivity, reliability, and scalability. For patients, these technologies translate into improved access, continuity, safety, and personalisation of care. For healthcare workers, they streamline workflows, facilitate collaboration, and support data-driven decision-making. The case of Asia illustrates the profound impact of multinetwork SIMs in bridging healthcare divides and reaching underserved populations. As the sector evolves, continued innovation and cross-sector collaboration will be key to unlocking the full potential of multinetwork IoT SIMs, building more resilient and patient-centred health systems worldwide.
Multinetwork IoT SIMs represent a paradigm shift in telemedicine and remote healthcare, offering unparalleled connectivity, reliability, and scalability. For patients, these technologies translate into improved access, continuity, safety, and personalisation of care. For healthcare workers, they streamline workflows, facilitate collaboration, and support data-driven decision-making. The case of Asia illustrates the profound impact of multinetwork SIMs in bridging healthcare divides and reaching underserved populations. As the sector evolves, continued innovation and cross-sector collaboration will be key to unlocking the full potential of multinetwork IoT SIMs, building more resilient and patient-centred health systems worldwide.  Multinetwork IoT SIMs represent a paradigm shift in telemedicine and remote healthcare, offering unparalleled connectivity, reliability, and scalability. For patients, these technologies translate into improved access, continuity, safety, and personalisation of care. For healthcare workers, they streamline workflows, facilitate collaboration, and support data-driven decision-making. The case of Asia illustrates the profound impact of multinetwork SIMs in bridging healthcare divides and reaching underserved populations. As the sector evolves, continued innovation and cross-sector collaboration will be key to unlocking the full potential of multinetwork IoT SIMs, building more resilient and patient-centred health systems worldwide.
Multinetwork IoT SIMs represent a paradigm shift in telemedicine and remote healthcare, offering unparalleled connectivity, reliability, and scalability. For patients, these technologies translate into improved access, continuity, safety, and personalisation of care. For healthcare workers, they streamline workflows, facilitate collaboration, and support data-driven decision-making. The case of Asia illustrates the profound impact of multinetwork SIMs in bridging healthcare divides and reaching underserved populations. As the sector evolves, continued innovation and cross-sector collaboration will be key to unlocking the full potential of multinetwork IoT SIMs, building more resilient and patient-centred health systems worldwide. Contact us
Are you looking for seamless connectivity, strong security, and flexible solutions for your next project? Our multinetwork smart cards boost reliability and control for POS terminals and IoT systems. Enjoy more uptime, easy management, and adaptability as technology changes.
Contact us to see how our smart cards can solve connectivity issues, lower costs, and enhance your customer experience. Let’s discuss your project and find the right fit for your needs.
Request a trial of our multinetwork SIMs to experience improved connectivity, greater uptime, and easier management for your operations. See how our solutions can cut costs, enhance security, and flexibly support your evolving business needs before making a long-term decision.
Contact us today to arrange your free trial and see for yourself how multinetwork SIMs can transform your POS terminals and IoT deployments, providing greater reliability and control from day one.
